A General Motors (GM) assembly plant based in Lake Orion, Mich., is ranked as the eighth largest user of green power generated onsite in the United States among the Environmental Protection Agency’s Green Power Partnership (GPP) partners. Over half of the automaker’s plant is powered by methane captured from a nearby landfill.
Orion Assembly, where GM’s Chevrolet Bolt EV is built, saves $1 million a year by using renewable energy. The plant also is home to a 350-kilowatt solar array that sends energy back to the grid.
The EPA launched the GPP in 2001 to increase the use of renewable electricity in the U.S. It is a voluntary program that encourages organizations to use green power as a way to reduce the environmental impacts associated with conventional electricity use, according to the EPA website.
Waste360 recently sat down with Rob Threlkeld, global manager of renewable energy for General Motors based in Detroit, Mich., to discuss the company’s use of renewable energy.
Waste360: What is the process or technology used to capture the methane?
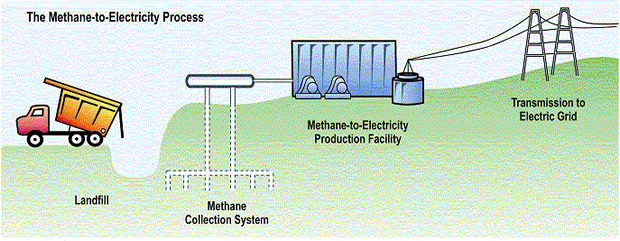
Rob Threlkeld: Landfill gas wells are installed in the landfill to capture the methane. A vacuum pulls the gas from the well through a pipe system. The gas is compressed and dried and sent to GM Orion Assembly to generate electricity. The compressed landfill gas is burned in on site generators to make electricity.
Waste360: How much energy is created and how is it used?
Rob Threlkeld: Orion Assembly generates up to 8 megawatts of electricity from landfill gas and that electricity powers the plant. Orion is producing 54 percent of its own electricity instead of buying it from a utility.
Waste360: Which landfills does the methane come from and what are their histories?
Rob Threlkeld: The landfill gas used at Orion Assembly comes from two nearby landfills, Eagle Valley, which is owned by Waste Management, and Oakland Heights Landfill, which is owned by Republic Services.
We’ve been pulling landfill gas from both landfills since 2002 to generate steam for heating and cooling. We’ve since reduced steam loads to the plant by improving the facility’s energy efficiency. In 2014, we started producing electricity from landfill gas on site. Fifty-four percent of the site’s electricity consumption comes from landfill gas. Both landfills are still open.
Waste360: Why did GM decide to become an Environmental Protection Agency’s Green Power Partnership Partner?
Rob Threlkeld: We decided to become an EPA Green Power Partner to help show our leadership position in the renewable energy space and demonstrate the benefits of using renewable energy, including reduced energy costs and reduced CO2 emissions.
Waste360: How does the program benefit GM?
Rob Threlkeld: The GPP provides a third party stamp of our leadership in the renewable energy space to address climate change and reduce energy costs. We’re also eager to promote the use of renewable energy and make the case that other corporations, big and small, can use it, too. Being a Green Power Partner also provides tools and resources like communications assets, trainings and opportunities to connect with other partners.
Waste360: How many other GM plants use renewable energy?
Rob Threlkeld: Twenty-eight facilities use some form of renewable energy. Several sites, like Orion Assembly and Fort Wayne Assembly, source multiple types of renewable energy. Both of these facilities use landfill gas for electricity and host solar arrays. Combined, our facilities promote the use of 106 megawatts of renewable energy globally.
GM is a member of the Buyers Renewables Center and the Renewable Energy Buyers Alliance. These organizations aim to accelerate corporate renewable energy procurement to help address climate change. As a member of these groups, we can share best practices in renewable energy procurement with others who are looking to scale up.
Megan Greenwalt | Aug 02, 2016
Read the original article http://www.waste360.com/gas-energy/gm-plant-using-landfill-gas-produce-54-its-electricity?utm_test=redirect&utm_referrer