Watch the future become reality as two Back to the Future icons see trash get turned into fuel for a car! And some people believe biodegradation doesn’t happen in a landfill. Silly them, this must seem like pure magic….
Category Archives: Latest Blogs

When Should You Not Recycle?
By Robert Coolman
Reduce, reuse, recycle—but for environmentalists, that’s not always a good idea.
When is it right to recycle? If your answer is “always,” I plead with you to re-evaluate your priorities as an environmentalist. We certainly have an obligation to use Earth’s resources and manage waste responsibly, but I believe the priorities and practices of modern environmentalism are in serious need of introspection.
Films like “Wall-E” and “Idiocracy” would have you believe that we are only years away from skyscrapers of garbage on the outskirts of our cities, but the truth is landfill capacity isn’t a problem in the foreseeable future. According to a letter in Nature Climate Change, U.S. landfills have an average of 34 years of capacity remaining, though capacity is growing at a rate of 2.7 years annually. Also, it’s not as if that land is unusable once it’s filled. Much of NYC is built on top of garbage, and so are many parks. Local governments are typically upfront about what places were formerly landfills (here’s mine) and continually monitor methane gas and liquid leachate levels, concerns that modern landfills are specifically engineered to manage.
To say that landfill space isn’t a problem in the foreseeable future isn’t to say we shouldn’t think about it at all. Rather, there are concerns that will cause much larger problems much, much sooner. Because we are already seeing the effects of climate change due to the increase in greenhouse gases, the right time to recycle is when it reduces greenhouse gas emissions. If landfills can be used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we should absolutely use them.
Recycling the hard-to-find elements put in many electronics is a no-brainer. Energy, pollution, and money are also all saved when comparing the reprocessing of post-consumer metal scrap against mining and processing ore. As for other stuff? With one major exception, it should all be landfilled.
A common criticism of landfills is how long it takes materials to break down. Ironically, this is backwards; it’s the materials that break down fastest that we should be most concerned about. When organic materials like food, yard waste, and biodegradable plastics break down in a landfill, they anaerobically decompose to produce methane. This is a problem because methane is more than 20 times potent as a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, which is what organic matter turns into when it composes aerobically in a composter.
There’s two ways to solve this methane problem. First is to capture the methane produced from a landfill and burn it. This turns the methane into carbon dioxide and can generate electricity. While this is the traditional method, it only works after a landfill has been capped. According to Waste Consultant and Yale Student Jon Powell, “91 percent of all landfill methane emissions are due to landfills that are still open.” Additionally, the infrastructure to produce electricity from combusting methane is subject to a cost/benefit analysis of how much methane is produced and for how long.
The alternative is to separate out organic matter from other landfilled solids, then intentionally turn it into methane which can be turned into electricity at an even greater return. Because the carbon contained in biomass (and by extension the carbon in the gases that evolve from it) was brought out of the atmosphere by plants performing photosynthesis on atmospheric carbon dioxide, returning bio-based carbon to the atmosphere (specifically in the form of carbon dioxide) does not contribute to the total amount of atmospheric carbon, and thus does not contribute to climate change.
So now we’re up to four bins: electronics, metal, biodegradable stuff (including most paper), and everything else. The “everything else” bin goes directly to the landfill, and includes both plastic and glass. Recycling glass is so close to a borderline energy improvement that it probably doesn’t deserve its own bin. As for plastic, anything that’s not code 1 (rPET) can’t be recycled to make containers and is instead demoted to plastic lumber, etc. When it’s done being that, it’s almost certainly going to the landfill anyway.
Why not incinerate used plastics to produce energy? The atoms in plastic come from petroleum, so burning plastic still counts as a fossil fuel and creates a net increase greenhouse gases. In a landfill, the carbon in plastic is said to be “sequestered” which is the end goal of taking carbon out of the air and storing it so it won’t reach the atmosphere. Methods of sequestering atmospheric carbon are still under development and inherently take lots of energy; more energy than we got from burning the plastic in the first place. Instead of (1) burning plastic (2) taking the released carbon out of the air at great energy cost and (3) sequestering it, it’s probably best just to leave it sitting in a landfill.
Read original post here: http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2015/10/24/reduce-reuse-recycle-but-not-always.html
This was a great article and shows that the author has a pretty good understanding of the realities of recycling. In my time I have run across a handful of people that are misguided in their belief that we should recycle everything. When you hear someone say this you can rest assured that the person making that statement lacks the understanding and knowledge about the realities of recycling. And unfortunately, many people mistakenly quote countries out of the EU as recycling rates as high as 80%. Many of these countries include incineration in their recycling numbers.
Unfortunately those that may think we should recycle everything throw out inaccurate and misleading recycling rates out into the public domain to get others to believe the same misguided and environmentally and economically detrimental approach to our waste. In the meantime, there are companies like ENSO Plastics who understand the realities of our waste infrastructures and is working diligently to develop solutions that will make the most environmental impact today.
Click here to download a free white paper on how to develop sustainability strategies of reaching zero waste; https://ensoplastics.com/download/Plastics_EstablishingthePathtoZeroWaste.pdf
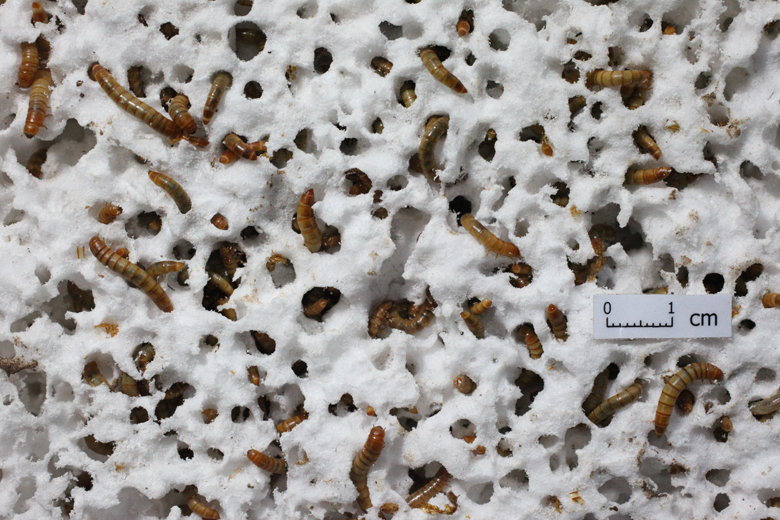

Plastic-eating worms may offer solution to mounting waste, Stanford researchers discover
An ongoing study by Stanford engineers, in collaboration with researchers in China, shows that common mealworms can safely biodegrade various types of plastic.
By Rob Jordan
Mealworms munch on Styrofoam, a hopeful sign that solutions to plastics pollution exist. Wei-Min Wu, a senior research engineer in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, discovered the larvae can live on polystyrene. (Photo: Yu Yang)
Consider the plastic foam cup. Every year, Americans throw away 2.5 billion of them. And yet, that waste is just a fraction of the 33 million tons of plastic Americans discard every year. Less than 10 percent of that total gets recycled, and the remainder presents challenges ranging from water contamination to animal poisoning.
Enter the mighty mealworm. The tiny worm, which is the larvae form of the darkling beetle, can subsist on a diet of Styrofoam and other forms of polystyrene, according to two companion studies co-authored by Wei-Min Wu, a senior research engineer in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Stanford. Microorganisms in the worms’ guts biodegrade the plastic in the process – a surprising and hopeful finding.
“Our findings have opened a new door to solve the global plastic pollution problem,” Wu said.
The papers, published in Environmental Science and Technology, are the first to provide detailed evidence of bacterial degradation of plastic in an animal’s gut. Understanding how bacteria within mealworms carry out this feat could potentially enable new options for safe management of plastic waste.
“There’s a possibility of really important research coming out of bizarre places,” said Craig Criddle, a professor of civil and environmental engineering who supervises plastics research by Wu and others at Stanford. “Sometimes, science surprises us. This is a shock.”
Plastic for dinner
In the lab, 100 mealworms ate between 34 and 39 milligrams of Styrofoam – about the weight of a small pill – per day. The worms converted about half of the Styrofoam into carbon dioxide, as they would with any food source.
Within 24 hours, they excreted the bulk of the remaining plastic as biodegraded fragments that look similar to tiny rabbit droppings. Mealworms fed a steady diet of Styrofoam were as healthy as those eating a normal diet, Wu said, and their waste appeared to be safe to use as soil for crops.
Researchers, including Wu, have shown in earlier research that waxworms, the larvae of Indian mealmoths, have microorganisms in their guts that can biodegrade polyethylene, a plastic used in filmy products such as trash bags. The new research on mealworms is significant, however, because Styrofoam was thought to have been non-biodegradable and more problematic for the environment.
Researchers led by Criddle, a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment, are collaborating on ongoing studies with the project leader and papers’ lead author, Jun Yang of Beihang University in China, and other Chinese researchers. Together, they plan to study whether microorganisms within mealworms and other insects can biodegrade plastics such as polypropylene (used in products ranging from textiles to automotive components), microbeads (tiny bits used as exfoliants) and bioplastics (derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn or biogas methane).
As part of a “cradle-to-cradle” approach, the researchers will explore the fate of these materials when consumed by small animals, which are, in turn, consumed by other animals.
Marine diners sought
Another area of research could involve searching for a marine equivalent of the mealworm to digest plastics, Criddle said. Plastic waste is a particular concern in the ocean, where it fouls habitat and kills countless seabirds, fish, turtles and other marine life.
More research is needed, however, to understand conditions favorable to plastic degradation and the enzymes that break down polymers. This, in turn, could help scientists engineer more powerful enzymes for plastic degradation, and guide manufacturers in the design of polymers that do not accumulate in the environment or in food chains.
Criddle’s plastics research was originally inspired by a 2004 project to evaluate the feasibility of biodegradable building materials. That investigation was funded by the Stanford Woods Institute’s Environmental Venture Projects seed grant program. It led to the launch of a company that is developing economically competitive, nontoxic bioplastics.
Co-authors of the papers, “Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms. 1. Chemical and Physical Characterization and Isotopic Tests” and “Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms. 2. Role of Gut Microorganisms,” include Yu Yang, Jun Yang, Lei Jian, Yiling Song and Longcheng Gao of Beihang University, and Jiao Zhao and Ruifu Yang of BGI-Shenzhen.
Click here to read the original article: https://news.stanford.edu/pr/2015/pr-worms-digest-plastics-092915.html
This paper is really fascinating as it moves us forward in helping the mainstream understand the importance of microbes in dealing with waste. The earth has been around for billions of years, with microbes having been here for the past millions. These microscopic organisms are very adaptable and I believe will continue to show their importance with helping humans deal with the pollution that we generate. All animals create waste of some kind and these little guys are here to help break down that waste into the building blocks of nature. Its the same concept that ENSO has pursued since our beginnings; use nature as an example of how to manage waste.

Landfill biomethane to fuel 400 UPS vehicles across California
CALIFORNIA, US
American courier United Parcel Service (UPS) has signed a partnership with Clean Energy Fuels for the supply of biomethane for its delivery fleet across California.
Beginning this month, UPS fuelling stations in Sacramento, Fresno and Los Angeles will use renewable natural gas (RNG), known as Redeem, for refueling tractors and delivery vehicles.
The three stations are expected to provide approximately 1.5 million gallon equivalents annually of RNG fuel to nearly 400 UPS CNG vehicles in California.
The deal falls in line with UPS’ goal of driving one billion miles using alternative fuel and advanced technology fleet by the end of 2017.
RNG, also known as biomethane, can be derived from sources including decomposing organic waste in landfills, wastewater treatment and agriculture.
Mitch Nichols, UPS senior vice president of transportation and engineering, said: “Renewable natural gas is critical to our effort to minimize UPS’s environmental impact while meeting the growing demand for our services.”
Harrison Clay, president. Clean Energy Fuels, said: “This step by UPS sends a clear message that RNG is a viable, cost-effective alternative to traditional diesel.”
UPS currently operates natural gas tractors on RNG in the UK, through a partnership with Mercedes Benz.
Read the original article here: http://www.waste-management-world.com/articles/2015/05/landfill-biomethane-to-fuel-400-ups-vehicles-across-california.html?cmpid=EnlWMW_WeeklyMay72015
###

Sweden recycles 99% of Waste?
Today I ran across an article claiming that Sweden now recycles 99% of all it’s waste. Interested to learn how the Swede’s had figured out the recycling conundrum the rest of the world faces, I delved into the article. To my dismay, this was clever redirecting and marketing. Somehow it is now considered recycling to burn trash??
http://truththeory.com/2014/09/17/sweden-is-now-recycling-99-percent-of-its-trash-heres-how-they-do-it/
Sweden does have high recycling rates (in the traditional definition of recycling), here are the 2013 figures:
Material Percentage
Glass 89.00 %
Cardboard 77.20 %
Metal 73.10 %
Plastic 36.70 %
Drinking containers 88%
Biodegradable food waste 13.5 %
Office paper 66%
Batteries 65%
More sources of statistics can be found here (summary in swedish): http://www.sopor.nu/Rena-fakta/Avfallsmaengder/Statistik
However, when did we redefine recycling to include incineration? There is no environmental benefit to redefining verbiage to skew the data and make ourselves feel better. Let’s just stick with the actual facts and forget the clever re-directions: Sweden recycles about 49% of their trash, they incinerate about 50% and the remaining is landfilled. No sugar coating needed.
Fungus Discovered in Rainforest Capable Of Eating Plastic Pollution
One of the biggest problems facing the earth, plastic pollution, could soon meet its match if students at Yale University are able to breed a recently discovered plastic-eating fungus on a large scale.
Plastic pollution, exemplified by the giant floating island of trash the size of Texas in the Pacific ocean, is highly detrimental to the world’s ecosystem because it breaks down extremely slow. In fact, according to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, plastic doesn’t actually biodegrade:
“Plastics do not biodegrade, although, under the influence of solar UV radiations, plastics do degrade and fragment into small particles, termed microplastics.”
This presents humans with a challenge that must soon be met, considering much of our plastic trash ends up in the ocean where it breaks down into toxic microplastics, winding up in sea life. Not only is this dangerous to the sea life, but it’s also dangerous to people because we end up consuming these very fish which we are poisoning with our trash.
Many groups and organizations have been formed to clean up plastic that ends up washing ashore on our beaches, but the vast majority of plastic pollution ends up in the ocean. The planet has a growing addiction to cheap and industrious plastic, increasing in use exponentially every year with no end in sight.
This is why the discovery of plastic-eating fungus is so exciting. According to Inhabitat,
On an expedition to the rainforest of Ecuador, students from Yale’s Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry discovered a previously unknown fungus that has a healthy appetite for polyurethane. According to Fast Company, the fungus is the first one that is known to survive on polyurethane alone, and it can do so in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment, which suggests that it could be used at the bottom of landfills.
The discovery was published in the scientific journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Researchers were also able to isolate the enzyme responsible for decomposing the plastic.
It isn’t exactly clear how this fungus will be implemented in bioremediation, but one can picture floating plastic islands covered in mushrooms which will eat the entire trash pile then sink into the ocean.
It’s also important to wean ourselves away from petroleum based plastics because they require many resources just to manufacture, and pollution doesn’t start or end with the trash in the gutter. Many other sustainable options are available which could used instead, like hemp based or other plant based plastics.
Original article by Nick Bernabe on 28 August, 2014 at 02:20 http://themindunleashed.org/2014/08/fungus-discovered-rainforest-capable-eating-plastic-pollution.html
Microbes eating plastics in on our oceans may have a big impact
Microscopic creatures that live on tiny ocean plastics greatly affect the fate and ecological impacts of marine plastic pollution, according to researchers from The University of Western Australia.
PhD candidate Julia Reisser and colleagues have published an article in the international journal PLOS One that contributed many new records of microbes and invertebrates living on sand-sized marine plastics.
Winthrop Professor Chari Pattiaratchi, Ms Reisser’s PhD supervisor, said there were huge numbers of floating plastics at sea and the study was the first to document biological communities on pieces from Australian waters.
The tiny ocean plastics come from the breakdown of discarded plastic items, such as single-use packaging and fishing gear.
More than 1000 images were taken while examining ocean plastics from Australia-wide sample collections using a scanning electron microscope at UWA’s Centre for Microscopy, Characterisation and Analysis.
The good news is that some of the plastic inhabitants may decrease plastic pollution level at the sea surface, where major environmental impacts occur.
Study co-author Dr Jeremy Shaw said large numbers of silica-forming algae weighed down their plastic host, potentially causing tiny pieces to sink to the bottom of the ocean.
The researchers were also able to see colonies of microbes that seem to be “eating plastics”.
“Plastic biodegradation seems to happen at sea. I am excited about this because the ‘plastic-eating’ microbes could provide solutions for better waste disposal practices on land,” Ms Reisser said.
Read the original article here: http://www.news.uwa.edu.au/201406186770/research/tiny-plastic-dwellers-have-big-impact-our-oceans
This is extremely interesting research! It is very important for the human race to better understand what is happening in our oceans and other marine environments as it relates to plastics. More and more research is showing how microbes are able to adapt to their environmental conditions to naturally break down compounds back into the building blocks that nature works with.
This research and others like it will help educate the public about the amazing abilities of those tiny unseen microbes. Its not magic its science, and from research like this as well as many others we will begin to develop a better and more detailed understanding of how microbes (who out number the inhabitants of the planet in a single handful of soil) are always working to restore balance in nature.
It’s time for U.S. employers to go green
By Margaret Badore
A survey released yesterday shows that many Americans want their workplaces to be more environmentally sustainable, and employers should take note.
The survey was commissioned by Ricoh Americas and conducted by Harris Polls. The survey of 948 employees, people defined as having part-time and full-time work, aimed to measure how much people care about their company’s sustainability practices.
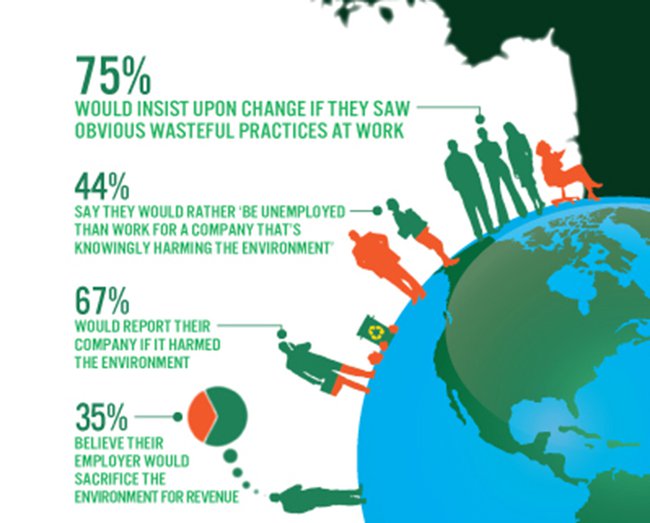
The poll found that three out of four employees said they would insist on change if they saw an obviously wasteful practice at work. Sixty-seven percent said they would report if their company were harming the environment.
Perhaps most surprisingly, 44 percent of respondents said they’d rather be unemployed than work for a company that knowingly harms the environment. “People do not want to be associated with a company that is knowingly damaging the environment,” said Jason Dizzine, director or technology marketing at Ricoh. He also points out that the phrasing of the question regarding unemployment is very specific. “It’s not that they’d rather be unemployed than work for a company that doesn’t have the strongest environmental policy.”
It should be noted that the survey aimed to measure workers’ general attitudes towards sustainability, rather than look for their opinions on specific sustainability practices.
Many Americans feel that they are being more sustainable at home than at work, with 68 percent of respondents saying that they feel they do more for the earth at home than at work.
Although more than half (59 percent) of surveyed employees were optimistic about sustainability in the future, it’s clear that there’s still a lot of work to be done. Thirty five percent of employees think their companies would sacrifice the environment to increase profits and 18 percent said they’d seen an environmentally harmful activity at work.
“Employees are demanding these types of commitments to sustainability and environmental programs,” said Dizzine. He says that if companies want to attract top talent, adopting environmental practices is a good idea. It’s no longer just government regulations or even customers that should make companies care about sustainable practices. “I think it’s clear from this poll that employees are expecting us to take action as well.”
Read the original article here http://www.treehugger.com/corporate-responsibility/its-time-us-employers-go-green.html
My personal comments by Danny Clark
This past weekend I was in one of the largest retail chains in the world shopping for a few particular items. Being that it was Easter weekend, there was a very large display area filled with gifts and baskets. One thing that stood out in the center of this massive display, was an enormous mound of white plastic buckets. A pile so high of these plastic buckets; useable for making gift baskets and/or the obligatory Easter egg hunt. . There must have been hundreds of these white buckets at this particular store and I could only imagine that this same display was the same all over the country in each and every retail location. Thousands upon thousands of these plastic buckets that would ultimately be thrown in neighborhood trash cans in the next few days.
I happen to know this particular manufacturer and have worked with several people within their company. This particular manufacturer is one of the top five largest plastic manufacturers in the U.S. and produces millions of pounds of plastic items just like these one-time-use buckets. The majority of products produced by this manufacturer are one-time-use, non-recyclable, that will inevitably end up in landfills around the country.
What environmental mission would you expect from a company like this that produces millions of pounds of plastics and how should they take responsibility? This particular manufacturer suggests and supports the idea “that we all should recycle our plastics.” This is a great idea but does nothing to reduce the environmental impact this manufacturer places on the environment everyday by producing millions of pounds of plastic products that are destined for a landfill.
Somehow some companies have developed the notation that by simply stating “we support recycling” is somehow reducing their impact on the environment. I’m not sure that those who take this approach really truly understand what it means to take responsibility and take action to reduce their impact on the environment. One must actually do something; make a change in some way to start reducing their company’s environmental impact.
“Lobbing the turd,” by simply stating that your company supports recycling only makes the recycling issue someone else’s problem. In my opinion if these people within this manufacturer really supported recycling they would no longer produce a single product that didn’t have at least 30% recycled content. Imagine the change this would bring?
And what about using technologies such as ENSO RESTORE that bridge the gap between recycling and landfilling plastics? The technologies are out there that are better for the environment so it’s time to stop playing the “green” game by promoting an agenda that does nothing to reduce your company’s impact on the environment. Take responsibility by doing something to reduce the environmental impact your company places on the environment every day.
We all play an equally important part in solving the global plastic pollution problem, but it’s up to each of us to ask ourselves what we are doing to reduce our impact on the environment and then start doing something now to make a difference.

Are plastics the most sustainable packaging choice?
Six major categories of plastic packaging significantly reduce energy use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to packaging made with alternative materials, according to a new study.
Compiled by Franklin Associates for the American Chemistry Council and the Canadian Plastics Industry Association, and using 2010 as a baseline year, the data shows replacing plastic packaging with alternative materials would result in a 4.5 times more packaging weight, an 80 percent increase in energy use and 130 percent more global warming potential.
“The benefits hold up across a range of different kinds of applications and materials,” said Keith Christman, managing director of plastics markets for ACC. “Because plastics use so much less material in the first place it results in dramatic greenhouse gas reduction, and that’s just the start. It really adds up across the different types of packaging, to the equivalent of taking more than15 million cars off the road.”
The study pits the six major packaging resins — low density polyethylene, high density PE, polypropylene, PVC, polystyrene, expanded PS, PET — against paper, glass, steel, aluminum, textiles, rubber, and cork. It considers the implications of the materials used in caps and closures, beverage containers, other rigid containers, shopping bags, shrink wrap, and other flexible packaging in a detailed life cycle assessment.
Individual studies on particular products have been done before, Christman said, on products ranging from plastic pouches vs. cans for tuna and EPS vs. paper cups. But the new study, titled Impact of Plastics Packaging on Life Cycle Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the United States and Canada, is comparatively sweeping.
It contains more than 50 tables and 16 charts and illustrations and examines each of the major life cycle stages for packaging: raw material production, packaging fabrication, distribution transport, post-consumer disposal and recycling.
The study also offers a glimpse into the potential unintended consequences of proposed and recently enacted bans on plastic packaging products, Christman said. While a plastic bottle ban might keep bottles out of waterways, the increase in energy use to manufacture, transport and even recycle their glass counterparts would be dramatic, according to the numbers.
“I don’t think that’s what people intend by some of those policies,” Christman said. “But it could happen if policies force people back to alternatives that use more energy and produce more greenhouse gas emissions.”
Click here for the original Plastic News article.
By Gayle S. Putrich
Staff Reporter Plastics News
Published: March 14, 2014 12:29 pm ET

FTC Finds Company’s “Recyclability” Claims Misleading
Company’s Green Claims for Plastic Lumber Misleading
FTC Order Requires Firm to Have Distributors Take Down Ads With Unsupported Claims
A Wisconsin-based manufacturer of plastic lumber products has agreed to stop making allegedly unsubstantiated claims about the recycled content and recyclability of two of its brands of plastic lumber.
Under the FTC settlement, the company, N.E.W. Plastics Corp., must have credible evidence to support any recycling-related claims it makes, and is required to tell its distributors to remove any marketing material for the two products provided by the company before December 2013.
“Consumers deserve to know the truth about the products they are buying,” said Jessica Rich, Director of the Federal Trade Commission’s Bureau of Consumer Protection. “Many of them want to buy products that are environmentally friendly, but they can’t do that if they get information that’s wrong or unsupported.”
N.E.W. Plastics Corp., which also does business as Renew Plastics, is based in Luxemburg, Wisconsin, and makes plastic lumber products, including the Evolve and Trimax brands, which are used to make items such as outdoor decking and furniture. It sells the products to consumers through distributors.
In its administrative complaint, the FTC alleges that between September 2012 and March 2013, N.E.W. made false and misleading claims while promoting Evolve and Trimax. Specifically, the company claimed:
- * that Evolve products are made from 90 percent or more recycled content;
- * that Trimax products are made from mostly post-consumer recycled content; and
- * that both Evolve and Trimax are recyclable.
The proposed consent order prohibits N.E.W. from making any statements about the recycled content, post-consumer recycled content, or environmental benefits of any product or package unless they are true, not misleading, and are substantiated by competent and reliable evidence, which for some claims must be scientific evidence.
The proposed order also bars N.E.W. from making unqualified recyclable claims about any product or package, unless the product or package can be recycled in an established recycling program, and such facilities are available to at least 60 percent of consumers or communities where the product or package is sold. If N.E.W. can’t meet these requirements, it must qualify the claim regarding the availability of recycling centers. If only part of a product or package is recyclable, N.E.W. must disclose to consumers which part or portion of the product or package is recyclable.
Finally, the proposed order bars N.E.W. from providing anyone else with the means of making false, misleading, or unsubstantiated claims. The order will end in 20 years.
Information for Consumers
The FTC has new information for consumers in a blog post on its website. Also the FTC provides detailed guidance to businesses on environmental claims in its Green Guides.
To read the full article from the FTC go to http://www.ftc.gov/news-events/press-releases/2014/02/companys-green-claims-plastic-lumber-misleading