Let’s look at the issue of plastic waste and how we can use the circular economic model to resolve some of the problems that we face, that’s ultimately spilling into our environment. Some 300 million tons of plastic is manufactured globally each year and “plastic packaging” accounts for about 78 million tons of it. That’s 172 billion pounds of non-reusable, non-recyclable and unequivocally unaccounted for plastic waste. This includes items such as flexible packaging, films, foamed material, small items, contaminated material, complex/multi-layer applications and anything colored, where recycling and reusability are practically non-existent. These are single use, single cycle, applications. Also, there’s unanimous agreement that the vast majority of all these applications are destined for a landfill. And these are not the demonized landfills from days gone by; I’m talking about today’s modern landfills that are now energy generating power plants.
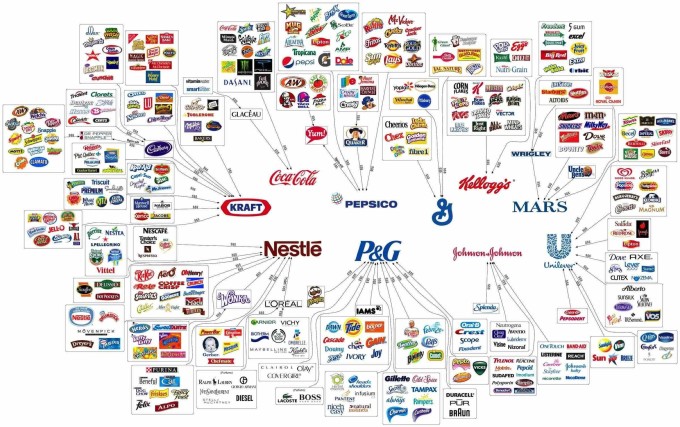
This discussion is not for the consumer, this is for the difference makers, the sustainability managers, the leaders that can make a difference. They’re the companies that, according to Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), are to be held accountable for the post-consumer aspect of its products and packaging. I’m talking about companies like Kraft, Coca-Cola, Nestle, PepsiCo, P&G, General Mills, Johnson & Johnson, Kellogg, Mars, Unilever and all the brands under them.
We all know, or the data tells us, that this is the single most common disposal method of all this material. It should also be known that waste-to-energy has proven to be one of our greatest resources for alternative energy. Whether it’s an anaerobic digester, a bioreactor or today’s modern landfills, most plastic packaging is ultimately ending-up in a unique anaerobic environment that is controlling and converting biogas into clean energy. Some of these companies utilize the energy from landfills, yet they haven’t put the pieces together to figure out that the very trash that their products produce could be the feedstock for the alternative energy resource they’re already harnessing. Too often, the end-of-life aspect is ignored or swept under the rug with theoretical contemplations about disposal methods that simply don’t exist and senseless confusion.
Yet, nearly all 50 states include landfill gas-to-energy as part of their green energy portfolios. It’s recognized by the United Nations, the EPA, as well as dozens of Fortune 500 companies and government organizations that all utilize energy from landfills. However, the dots just aren’t being connected. I recently asked the Director of Sustainability for one of these 10 companies about this topic and they honestly said that they’ve never heard of such a thing and can’t imagine that we’ll ever get our energy from slowly decomposing waste. Yet, three years ago this same company won top honors by the EPA as one of the largest on-site green power generators because of its use of Landfill Gas-to-Energy (LGE) to power its manufacturing facilities! Seriously, why the disconnect between what companies are doing and what companies should and could be doing to think more circular? Imagine if you will, this same company implementing landfill biodegradable packaging and then using the energy from landfill gas. This is true circular economy thinking, especially when energy needs will increase 50% in the next couple decades. Without requiring any change to the infrastructures in place today and without modifying consumer behavior, these single use applications can be designed to cycle at a higher level.
I’ve heard the idea that plastics should be made NOT to biodegrade in a landfill because one day we might want to mine for this material. This is completely asinine and assumes that we’ll have a need to mine for this material within the next couple hundred years. The reason being, plastic will eventually biodegrade, we just won’t be able to capture the gases produced if we wait too long. Instead, if these applications were designed to biodegrade within the managed timeframe of these anaerobic environments, for every million pounds of plastic waste that enters a LGE facility, it offers the equivalence of over 422,000 pounds of coal, 52,000 gallons of gasoline and more than 1100 barrels of oil, which is used to power homes and factories, as well as fueling vehicles!
The technology is readily available to make most any polymer application anaerobically biodegradable, or commonly referred to as Landfill Biodegradable. The technology does not change any processing parameters, there’s no change in any performance characteristics, and it’s not expensive. In fact, for about the price of a Tall Cappuccino, tens of thousands of Starbucks Coffee cups can be designed to biodegrade in a landfill. These multi-layer applications are not being reused or recycled, but they are going to a landfill. So what gives, is it because of the misguided concept that landfills are bad? Perhaps it’s time to reevaluate the integral role of this disposal method that rely so heavily on; a lot has changed since the 80’s. In fact, you could say that we’re now diverting 75% of all MSW away from landfills, because the type of landfills that are being vilified are becoming obsolete – quickly.
A single loop system for handling our plastic waste is impractical, circularity does not mean singularity, there’s too much at stake, too much potential, and the infrastructure is already in place so there’s no need to implement Cass Sunstein’s “nudging” tactics to change consumer behavior. Besides, the fact that none of this material can/will be recycled is not because of consumer behavior, its feasibility and market demand, and it’s just not there. A company wanting to take accountability for its packaging needs to answer one candid question: What is the common disposal method of the application? Then, do what can be done to take advantage of this fact and understand the value in having our waste integrate into our waste infrastructures instead of working against it. The facts, the science and all the data, prove that there’s an enormous opportunity being overlooked. I believe the circular economic model can work for plastics, but not if it’s simply a rebranding of the last 40+ years of rhetoric.